Plasma EVM Smart Contracts
This document describes contract implementation without continuous rebase which is currently work in progress.
You can check the source code of contracts used in Plasma EVM here
Contract Diagram
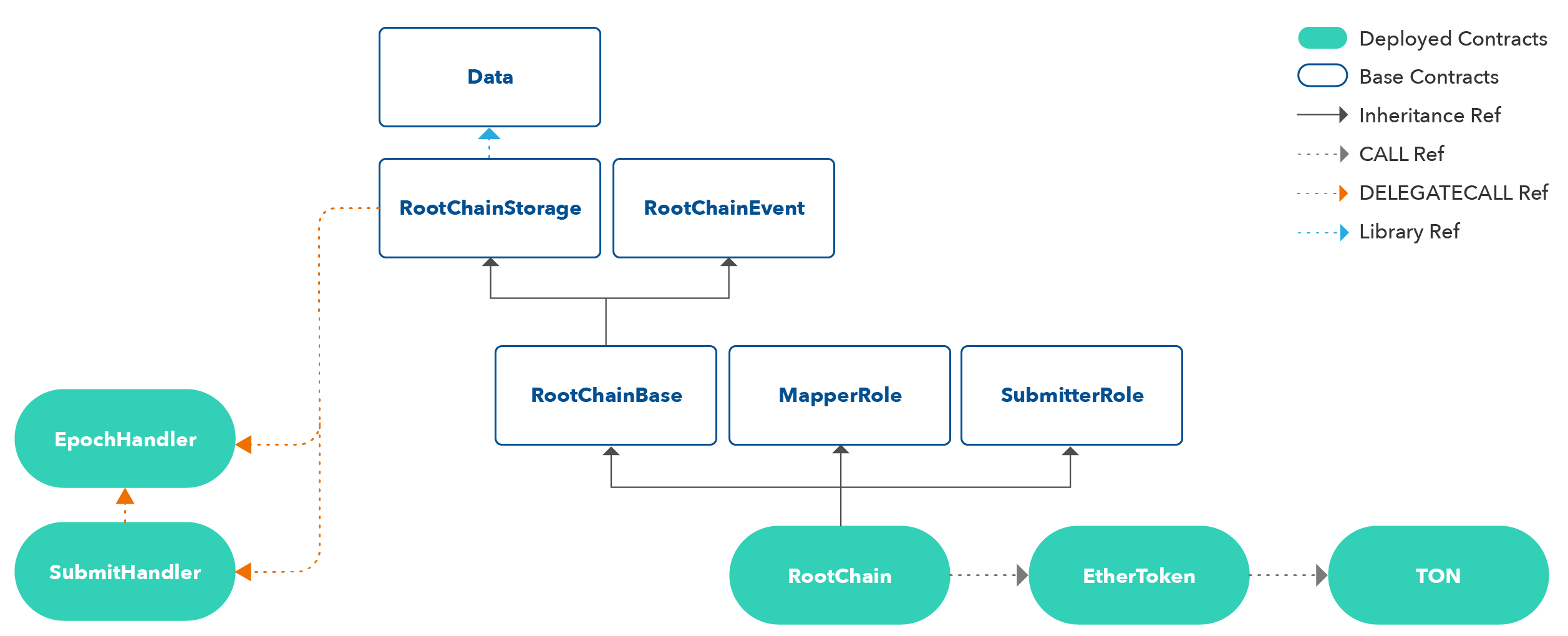
Box means contract implementation, solid line means inheritance relationship, black dotted line means reference relationship with CALL, blue dotted line means library reference. Green square means contract deployed on the network. Because the size of RootChain contract is large, we split it to EpochHandler and SubmitHandler, and connect them to handler contract by DELEGATECALL.
Contracts in this diagram have following features:
Data
Data implements structs and internal componenets used in Plasma EVM such as Epoch, PlansmaBlock, Request, RequestBlock, Transaction. In particular, it manages internal logic, e.g convert Request to RequestTransaction, compute transactionsRoot of RequestBlock. Constants managed by Data are as follows:
address public constant NA = address(0)Address of null address,
msg.senderof request transaction in child chain must beNA.uint public constant NA_TX_GAS_PRICE = 1e9tx.gasPriceof request transaction is always 1 Gwei.uint public constant NA_TX_GAS_LIMIT = 100000Gas limit of request transaction is always 100,000.
RootChainStorage
RootChainStorage is contract that only implements state variables. Key variables are as follows:
address operator: Operator account of child chain.operatorhandles authority management for block submission, requestable contract mapping of both chains, and operator account change.address epochHandler:EpochHandlercontract address referred byDELEGATECALLaddress submitHandler:SubmitHandlercontract address referred byDELEGATECALLaddress etherToken: ERC20 token contract in root chain corresponding to PETH of child chain.mapping (address => address) requestableContracts: Mapping of requestable contracts of root and child chain.uint NRELength: Length ofNREdetermined in deployingRootChain.uint currentFork: Current fork number. It is identical to cycle number in continuous rebase.Data.Request[] EROs: Array of enter and exit requests. Index range ofEROs, to be includednth RE, is determined whenn-3th NRE is submitted.RootChaincontract manages range of requests to be applied to child chain through this.Data.RequestBlock[] ORBs: More than one RB can be included in RE. Due to gas limit of child chain, number of requests in RB has limits. Therefore,ORBsis used for managing index range ofEROsin RB andtransactionsRootof the request transactions.uint lastAppliedForkNumber: Fork number that applied the last request.uint lastAppliedEpochNumber: Epoch number that applied the last request.uint lastAppliedBlockNumber: Block number that applied the last request.uint EROIdToFinalize: Index ofEROsto be applied next.
RootChainEvent
RootChainEvent is a contract that only implements events of RootChain.
RootChainBase is RootChainStorage, RootChainEvent
RootChainBaseinherits state variables and events from RootChainStorage and RootChainEvent. It has a function executing DELEGATECALL to EpochHandler and SubmitHandler.
SubmitHandler
submitNRE(uint256,uint256,bytes32,bytes32,bytes32): Function to submitNREcalled byRootChain.submitORB(uint256,bytes32,bytes32,bytes32): Function to submitNREcalled byRootChain.
EpochHandler
prepareORE(): Function preparing to submit nextREwhenSubmitHandlersubmitsNRE.prepareNRE(): Function preparing to submit nextNREwhenSubmitHandlersubmits lastRB.
SubmitHandler is RootChainBase
SubmitHandler is a contract for submitting blocks and epoch such as NRE, RB, etc. The contract reads EpochHandler to proceed to the next epoch. The following two functions are called only by Submitter.
submitNRE(uint _pos1, uint _pos2, bytes32 _epochStateRoot, bytes32 _epochTransactionsRoot, bytes32 _epochReceiptsRoot)
pos1 is uint256 type variable which merged two uint128 variables, fork number and epoch number. pos2 is "start and end block number of epoch", also encoded in the same way. This function prepares epochNumber + 3th RE in the end of execution.
submitORB(uint _pos, bytes32 _statesRoot, bytes32 _transactionsRoot, bytes32 _receiptsRoot)
pos is uint256 type variable which merged two uint128 variables, fork number and epoch number. For RB, the function computes merkle root of request transactions corresponding to the index of EROs determined by RootChain. If the merkel root is not identical to _transactionsRoot, the transaction will be reverted.
EpochHandler is RootChainBase
EpochHandler is a contract that prepares the next epoch when NRE or last RB is submitted. In case of RE whose epochNumber is n, index of Requests to be included in the RE is determined as soon as n-3 NRE is submitted.
prepareORE(): Function called bySubmitHandlerto submitNRE.prepareNRE(): Function called bySubmitHandlerto submit lastRB.
RootChain is RootChainBase, MapperRole, SubmitterRole
RootChain is a contract that implements several features such as submit blocks and epoch, generate requests, finalize function and getter to read contract state. In order to manage authorities to map RequestableContract of both chains, the contract inherits MapperRole, and SubmitterRole for managing authority of submitting blocks and epoch. The following functions are implemented in 'RootChain'.
mapRequestableContractByOperator(): Function mapping requestable contracts of both chains. OnlyMappercan call this function.finalizeBlock(): Function to finalize submitted blocks. An internal function with the same feature is called when block or epoch is submitted.finalizeRequest(): When RB is finalized, requests included in the block has its challenge period. Requests can be finalized after this period. This function checks finalization of blocks and requests to apply exit request in root chain.challengeExit(): Start challenge against invalid exit request. It checks validity with proof that the request is reverted or not.challengeNullAddress(): Transactions of NRB must be normal transactions. In other words, transactions sent byNAcannot be included inNRB. This function manages challenges for invalidNRB.startExit(address _to, bytes32 _trieKey, bytes _trieValue): This generates new exit request._tois an address of requestable contract in root chain,_trieKeyand_trieValueare paramters for request.startEnter(address _to, bytes32 _trieKey, bytes _trieValue): This generates new enter request. Parameters are the same as instartExit.
